|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Indicators | Sri Lanka | UK |
| (area km2) | 65,610 | 244,100 |
| People | ||
| Human Development Index (HDI) | 90 (of 174) | 10th |
| Population (millions) | 19 | 58.5 |
| Population density (per km2) | 275.0 | 244.0 |
| Urban population (%) | 22.6 | 89.3 |
| Life expectancy (years) | 73.1 | 77.2 |
| Infant mortality (per 1000) | 17 | 6.0 |
| Growth rate (%) | 1.4 | 0.1 |
| Education | ||
| Adult literacy (%) | 90.7 | 99.0 |
| In primary education (%) | 99.9 | 99.9 |
| Economic, Health & Social | ||
| GNP (US$ per capita) | 800 | 20,870 |
| TV's (per 1000 people) | 82 | 612 |
| Radios (per 1000 people) | 201 | 1,433 |
| Daily calorie intake | 2,263 | 3,237 |
| Doctors (per 1000 people) | 23 | 164 |
| Main imports: |
| textiles and materials, petroleum, machinery, vehicles, building materials |
| Main exports: |
| textiles/clothing, tea, diamonds, rubber, general agricultural products |
| Main industries: |
| processing agricultural products (tea, rubber, coconuts), tobacco, textiles/clothing, cement, tourism. |
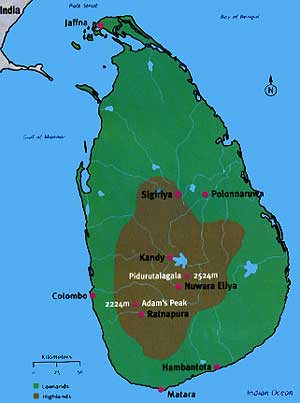
 Introduction  The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka was born in 1972. The country, formerly called Ceylon, became independent from the UK in 1948 and is a member of the Commonwealth. An island country to the south east of India, it covers an area of 65,610 km2 (just under a quarter the size of the UK), 400 kms in length and 200 kms at its widest in the south.
The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka was born in 1972. The country, formerly called Ceylon, became independent from the UK in 1948 and is a member of the Commonwealth. An island country to the south east of India, it covers an area of 65,610 km2 (just under a quarter the size of the UK), 400 kms in length and 200 kms at its widest in the south.
The island's distinctive pear shape is sometimes referred to as the 'Teardrop of India' or the 'Pearl of the Orient'. A flat plain stretches from the hill country northwards to the coast, covering about half of Sri Lanka. The south is mainly hilly, rising up to over 1500 metres to the highest point, Mt. Pidurutalagala (2524m), between the two plateau regions of Nuwaru Eliya and Horton Plains. Sri Lanka's famous tea plantations are found here, where the hot and humid climate experienced by the rest of the island gives way to cooler, less humid conditions.
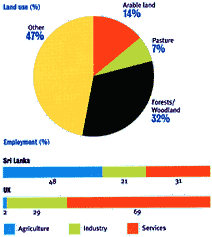
Sri Lanka's largest city is Colombo, the administrative capital, but over 75% of the population live in rural settlements. Traditionally the economy has been based on agriculture, employing almost 50% of the workforce. Many people are subsistence farmers, growing rice on small areas of land. Others work on plantations, concentrating on cash crops for export, especially tea, rubber and coconuts. Textiles and clothing are now the most important industries, especially in terms of export earnings.
|
Sri Lanka - general web sites:
|
 Brightly dressed baby elephant, Perahera festival in Kandy
Brightly dressed baby elephant, Perahera festival in Kandy