| Our
dependence on oil means that new discoveries can lead to huge
wealth. Much of the oil reserves are found in LEDCs.
But compared to LEDCs
with more diverse
economies, the countries that rely on selling oil have higher
levels of poverty. Six of the world’s oil-dependent
states are classified by the World Bank as highly indebted
poor countries. Roll over the icons to find out why.
Transnational
corporations have the infrastructure to drill, transport
and refine the oil in poorer countries. By getting a license
to extract the oil, transnational
corporations can make enormous profits.
 for
a table of the 15 transnational
corporations with the largest revenues. for
a table of the 15 transnational
corporations with the largest revenues.
How many corporations
involved in oil can you identify?
How many of the other corporations depend on oil in some way?
The rise of OPEC
In
the past, much of the oil industry and the prices paid
for oil were controlled by a handful of companies. But
in 1960, a new organisation was formed by a group of LEDCs
that relied heavily on selling oil. This was called the
‘Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries’,
or OPEC for short. OPEC members work together to control
the amount of oil pumped into the world marketplace by
agreeing supply quotas
of oil. This way, they aim to keep oil prices stable,
to guarantee themselves a steady income.
For more on oil and its effects on development, visit:
http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/business/3020185.stm
|
 for
a timeline of key moments in OPEC’s history. for
a timeline of key moments in OPEC’s history.
The
Price of Oil
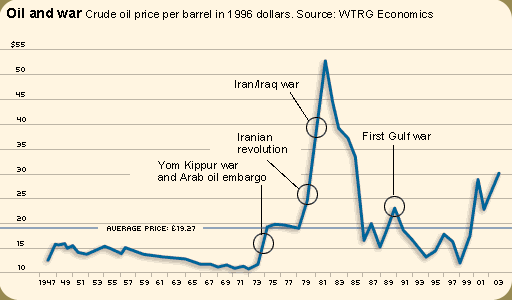
Countries that have no
oil of their own face problems when prices rise, especially
poorer countries.
 for some statements, and decide whether they describe an effect
of oil price rises on rich or poor countries. Drag them into
the correct column on the table.
for some statements, and decide whether they describe an effect
of oil price rises on rich or poor countries. Drag them into
the correct column on the table. |